WEB 开发中滚动条算是天天打交道了,大部分情况下是无感知的,需要的时候自动出现,不需要的时候绝对不会给你添乱。 但是好景不长,设计师丢给了你一个这样的滚动条,这不难为我嘛。
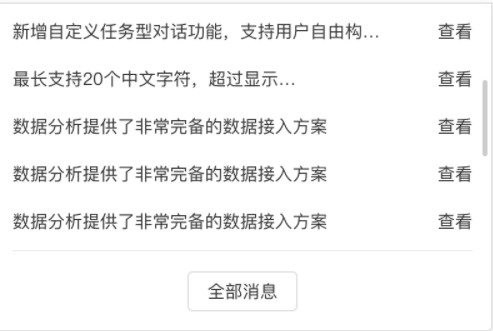
好在 webkit 内核的浏览器支持自定义滚动条,下面几个属性就能搞定了。不加选择器前缀的话则所有元素都生效, 如果只想某个区域生效加一个选择器前缀即可。
/* 滚动条宽和高,分别对应垂直滚动条和横向滚动条 */
::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 6px;
height: 6px;
}
/* 滚动条上的滚动滑块,设置背景色和圆角 */
::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
background: #CCCCCC;
border-radius: 6px;
}
/* 滚动条上的滑轨属性,设置背景色和其他属性 */
::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
background: transparent;
}
效果演示
# DIV + CSS 模拟滚动条
因为是 webkit 内核浏览器专属属性,所以在 IE 和 Firefox 上当然不支持了(Edge 由于已经采用了 chrome 内核, 所以也支持了)。既然如此只能另辟蹊径了,用 div + css 来模拟滚动条,然后监听原生滚动事件重置滚动条, 监听滚动条点击和拖拽事件模拟滚动。
# 计算滚动条宽度
默认情况下当出现滚动时浏览器会自动出现滚动条,我们的目标是模拟滚动条,那么肯定要把浏览器自带的滚动条隐藏掉。
比如在出现垂直滚动条时,假设滚动条宽度为 17px,那么设置滚动区域 margin-right: -17px; 即可把自带的滚动条隐藏了。
但是每个浏览器自带滚动条的宽度又不固定,只能用 js 动态获取了。
原理是通过 document.createElement('div') 新建一个 div,设置 visible 属性为 hidden,
这样就看不到了,但却真实存在。然后添加到 body 上,获取该 div 的 offsetWidth,
然后设置 overflow: scroll 强制该 div 出现滚动条。添加一个 div 到它内部去,获取内部 div 的 offsetWidth,
内外 div 的 offsetWidth 相减就得出了滚动条的宽度了,最后记得删除刚刚新建的 div,当做什么事都没有发生过一样。
// 获取滚动条宽度
getScrollbarWidth () {
const outer = document.createElement('div')
outer.style.visibility = 'hidden'
outer.style.width = '100px'
outer.style.position = 'absolute'
outer.style.top = '-9999px'
document.body.appendChild(outer)
const widthNoScroll = outer.offsetWidth
outer.style.overflow = 'scroll'
const inner = document.createElement('div')
inner.style.width = '100%'
outer.appendChild(inner)
const widthWithScroll = inner.offsetWidth
outer.parentNode.removeChild(outer)
this.scrollBarWidth = widthNoScroll - widthWithScroll
},
计算滑块高度,监听滚动事件,监听滑块点击事件和 move 事件等,嗨!不知道怎么用文字表述我的想法,
只能上代码大家自己看了,这里为了方便大家查看代码只写了垂直方向滚动条的效果,水平方向原理一样。
<template>
<div class="yi-scrollbar">
<!-- 外层容器,定义滚动范围 -->
<div class="yi-scrollbar__wrap" :style="wrapStyle" ref="wrap" @scroll="handleScroll">
<div class="yi-scrollbar__view" ref="view">
<!-- 容器通过插槽引入 -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 模拟滑轨和滑块 -->
<div
v-if="thumbVisible"
class="yi-scrollbar__track"
:class="{ visible: mouseDown }"
@mousedown.self="mousedownTrack">
<div
class="yi-scrollbar__thumb"
@mousedown="mousedownThumb"
:style="thumbStyle">
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
thumb: {
height: '0%',
translateY: '0%'
},
wrapHeight: 0,
viewHeight: 0,
mouseDown: false,
scale: 0,
init: {
clientY: 0,
scrollTop: 0
},
thumbVisible: false,
scrollBarWidth: 0
}
},
computed: {
thumbStyle: function () {
return {
height: this.thumb.height,
transform: `translateY(${this.thumb.translateY})`
}
},
wrapStyle: function () {
return {
marginRight: `-${this.scrollBarWidth}px`,
marginBottom: `-${this.scrollBarWidth}px`
}
}
},
mounted () {
this.getScrollbarWidth()
this.wrapHeight = this.$refs.wrap.clientHeight
this.viewHeight = this.$refs.view.clientHeight
// 只有在内层容器大于外层容器高度时才显示滚动条
this.thumbVisible = this.viewHeight > this.wrapHeight
this.calcThumbHeight()
},
destroyed () {
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', this.mouseupThumb, false)
},
methods: {
// 获取滚动条宽度
getScrollbarWidth () {
const outer = document.createElement('div')
outer.style.visibility = 'hidden'
outer.style.width = '100px'
outer.style.position = 'absolute'
outer.style.top = '-9999px'
document.body.appendChild(outer)
const widthNoScroll = outer.offsetWidth
outer.style.overflow = 'scroll'
const inner = document.createElement('div')
inner.style.width = '100%'
outer.appendChild(inner)
const widthWithScroll = inner.offsetWidth
outer.parentNode.removeChild(outer)
this.scrollBarWidth = widthNoScroll - widthWithScroll
},
// 计算滚动条滑块高度
calcThumbHeight () {
this.thumb.height = (this.wrapHeight / this.viewHeight) * 100 + '%'
const thumbHeight = this.wrapHeight * this.wrapHeight / this.viewHeight
// scrollTop 最大值 / 滑块可以滚动的距离,这样计算出滑块滑动距离后乘以该系数就能得到 scrollTop 值
this.scale = (this.viewHeight - this.wrapHeight) / (this.wrapHeight - thumbHeight)
},
// 监听滚动事件重置滚动条的Y轴偏移量
handleScroll (e) {
this.thumb.translateY = (e.target.scrollTop / this.wrapHeight) * 100 + '%'
},
// 监听鼠标在滑块上点击的事件
mousedownThumb (e) {
e.stopImmediatePropagation()
this.mouseDown = true
// 记录鼠标点击初始偏移量
this.init.clientY = e.clientY
this.init.scrollTop = this.$refs.wrap.scrollTop
// 事件添加到 document 上是为了拖拽滑块的时候鼠标移出内容区域也能响应事件
document.addEventListener('mousemove', this.mousemoveThumb, false)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', this.mouseupThumb, false)
// 在滚动的时候禁止选中文本
document.onselectstart = () => false
},
// 监听鼠标拖拽事件
mousemoveThumb (e) {
if (!this.mouseDown) return
// 当前鼠标位置减去初始鼠标位置得到鼠标拖拽的偏移量
const offset = e.clientY - this.init.clientY
// 鼠标拖拽偏移量乘以上面计算的系数得出 scrollTop
const scrollTop = offset * this.scale
// scrollTop 一定要加上初始 scrollTop
this.$refs.wrap.scrollTop = this.init.scrollTop + scrollTop
},
// 监听鼠标离开事件
mouseupThumb (e) {
this.mouseDown = false
this.init.scrollTop = 0
// 这里要移除拖拽事件,不然鼠标离开了有可能拖拽事件还在执行
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', this.mousemoveThumb, false)
document.onselectstart = null
},
// 监听滑轨点击事件,直接滚动到指定位置
mousedownTrack (e) {
// 鼠标在元素内偏移量为鼠标距离顶部的距离减去元素顶部偏移
const offset = e.clientY - e.target.getBoundingClientRect().top
// 根据鼠标点击位置偏移量计算 scrollTop
const scrollTop = (offset / this.wrapHeight) * this.viewHeight - this.wrapHeight / 2
this.$refs.wrap.scrollTop = scrollTop
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.yi-scrollbar {
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
&:hover {
.yi-scrollbar__track {
opacity: 1;
}
}
}
.yi-scrollbar__wrap {
overflow: auto;
height: 100%;
}
.yi-scrollbar__track {
position: absolute;
right: 4px;
top: 2px;
bottom: 2px;
width: 6px;
opacity: 0;
transition: opacity 120ms ease-out;
border-radius: 4px;
z-index: 1;
cursor: pointer;
&.visible {
opacity: 1;
}
}
.yi-scrollbar__thumb {
background-color: rgba(144,147,153,0.3);
cursor: pointer;
width: 100%;
transition: .3s background-color;
border-radius: 4px;
&:hover {
background-color: rgba(144,147,153,0.5);
}
}
</style>
怎么用呢?YiScrollbar 是上面写的组件。
<template>
<YiScrollbar class="demo2">
<div class="demo2-inner"></div>
</YiScrollbar>
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.demo2 {
height: 300px;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.demo2-inner {
height: 1200px;
background: linear-gradient(0deg, #ebeef7, #dab9b9);
}
</style>
来看看实际效果演示
